Introduction
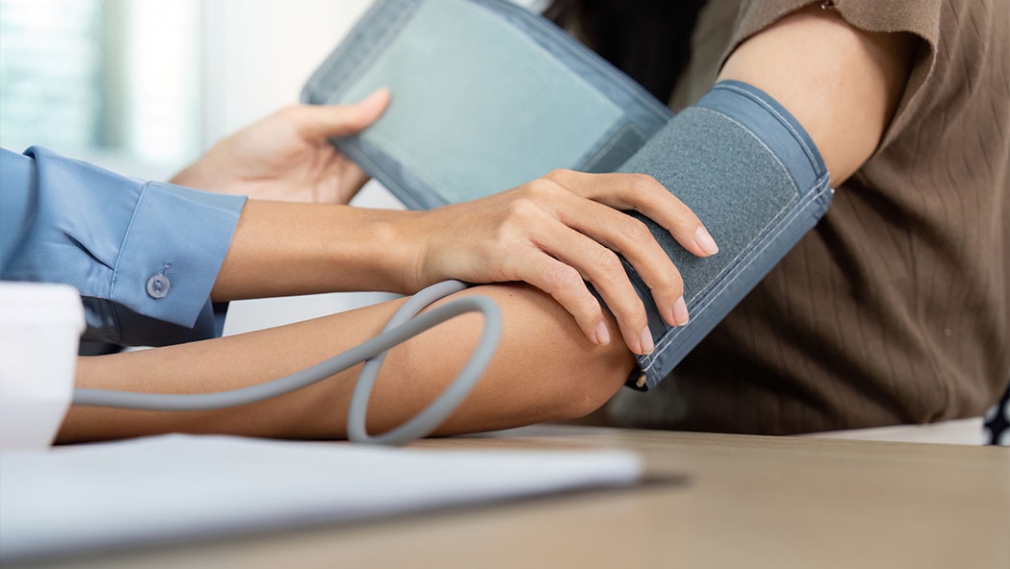
Hypertension is a serious chronic condition affecting over a billion people globally and is the leading risk factor for morbidity and mortality. Hypertension is often asymptomatic in the initial stages, making it crucial to recognize hypertension early to help mitigate disease progression.
Hypertension…